Définition
Le logarithme décimal, noté $\log$, est la fonction définie sur $]0~;~+\infty[$ par :
Pour tout $b > 0$, $\log(b)$ est l'unique solution de $10^x = b$.
Pour $x > 0$ et $a$ réel : $\log(x) = a \Leftrightarrow x = 10^a$.
Elle est strictement croissante sur $]0~;~+\infty[$.
Propriétés algébriques
Valeurs particulières
$\log(1) = 0$ donc log est négative sur $]0~;~1]$ et positive sur $[1~;~+\infty[$.
$\log(10) = 1$.
Propriétés de calcul
Pour tout $a$ et $b$ réels strictement positifs, et $n \in \mathbb{N}$ :
- $\log(a \times b) = \log(a) + \log(b)$
- $\log\left(\dfrac{1}{b}\right) = -\log(b)$
- $\log\left(\dfrac{a}{b}\right) = \log(a) - \log(b)$
- $\log(a^n) = n\log(a)$
Pour $a = 10$ : $\log(10^n) = n\log(10) = n$.
Équation et inéquation
Équation : $\log(a) = \log(b) \Leftrightarrow a = b$
Inéquation : $\log(a) \leq \log(b) \Leftrightarrow a \leq b$
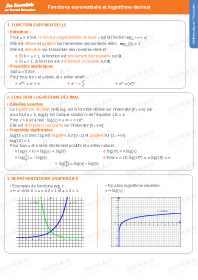
Représentation graphique

EN RÉSUMÉ